Session 3: Starting SuperTuxKart and controlling the car with ROS2
What We’ll Do
Start supertuxkart, start a race
Get camera image from supertuxkart
Using the camera image, make the car drive itself
Watch the car race on its own!
Compete with your friends to see who can make the fastest self-driving car
Downloading SuperTuxKart
Ubuntu 22 Terminal:
Install it by typing
sudo apt install -y ros-humble-supertuxkart.deb
In file properties mark it as an executable. Run the game by double-clicking on the supertuxkart.AppImage file.
You can also run the game in Web Browser by visiting SuperTuxKart. Note: This version does not support Multiplayer mode.
Starting the Game with ROS2
Open Ubuntu terminal and type:
ros2 run supertuxkart supertuxkart
After this, start the game and let’s check if everything is working. Open another terminal and type:
ros2 node list
You should see something like /stk_node. To inspect it, type:
ros2 node info /stk_node
You’ll see a list of topics and services that the game is using to communicate with ROS2.
Understanding the Output
The output of the ros2 node info /stk_node command will show you the topics that the game is listening to and the topics that the game is publishing to.
If you see something like this:
Subscribers:
/cmd_vel: geometry_msgs/msg/Twist
/stk_commands: std_msgs/msg/Int16MultiArray
It means that the game is listening for messages on those topics. The /cmd_vel topic is used to control the speed and direction, while /stk_commands is for sending multiple commands.
The type of message that the game is expecting is also shown. For example, the game is expecting a geometry_msgs/msg/Twist message on the /cmd_vel topic.
If we publish messages to /cmd_vel, the car will move in the game. For example:
ros2 run teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard
OR
pip3 install pygame
ros2 run supertuxkart teleop.py
This will allow you to control the car using the keyboard when the dialog box is in focus. Just like with the Turtlesim python code, you can also publish messages to SuperTuxKart using python. For example:
import rclpy
from rclpy.node import Node
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
class CarMover(Node):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__('car_mover')
self.publisher = self.create_publisher(Twist, "/cmd_vel", 1)
self.timer = self.create_timer(0.1, self.move_car)
def move_car(self):
twist_msg = Twist()
twist_msg.linear.x = 0.5
self.publisher.publish(twist_msg)
def main():
rclpy.init()
car_mover = CarMover()
rclpy.spin(car_mover)
rclpy.shutdown()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
The publishers section shows the topics that the game is sending messages to. For example:
Publishers:
/stk_image: sensor_msgs/msg/Image
Here, the game is sending images from the game to the /stk_image topic.
You can see the data received by subscribing to the topic. For example:
ros2 topic echo /stk_image
To visualize the image, you can use RQT Image Viewer and subscribing to the topic:
ros2 run rqt_image_view rqt_image_view
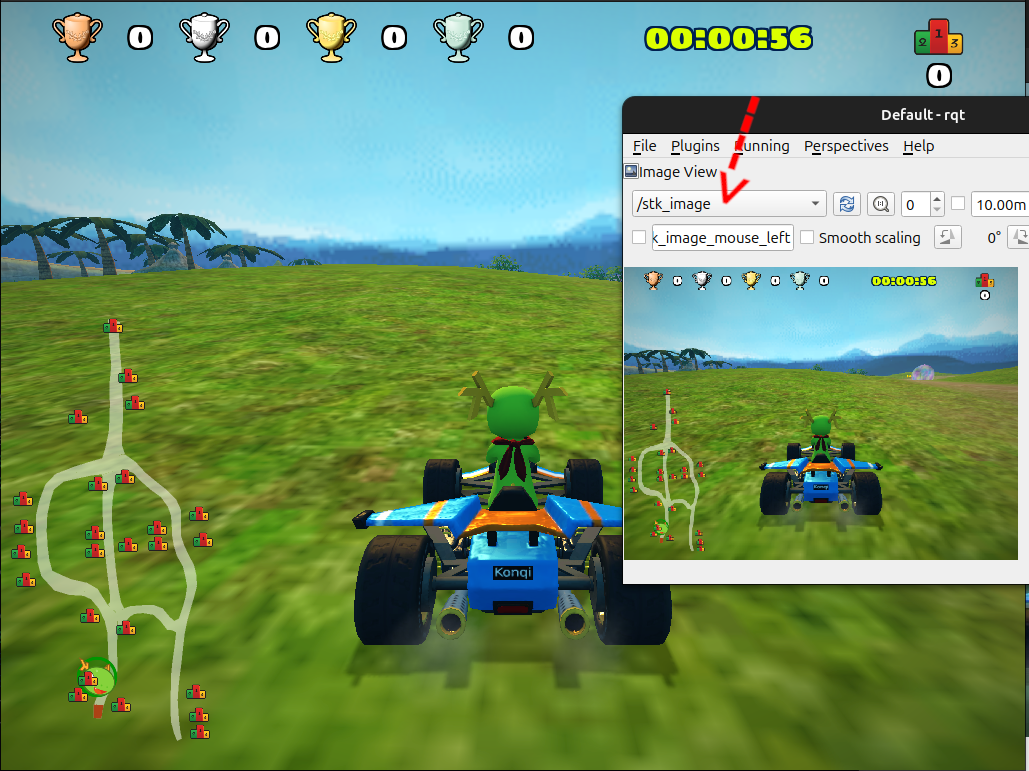
This will show you the image data that the game is sending to ROS2.
In the next session, we’ll access the game image and use OpenCV to make the car drive by itself.